TCP와 UDP
10 Jun 2017TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
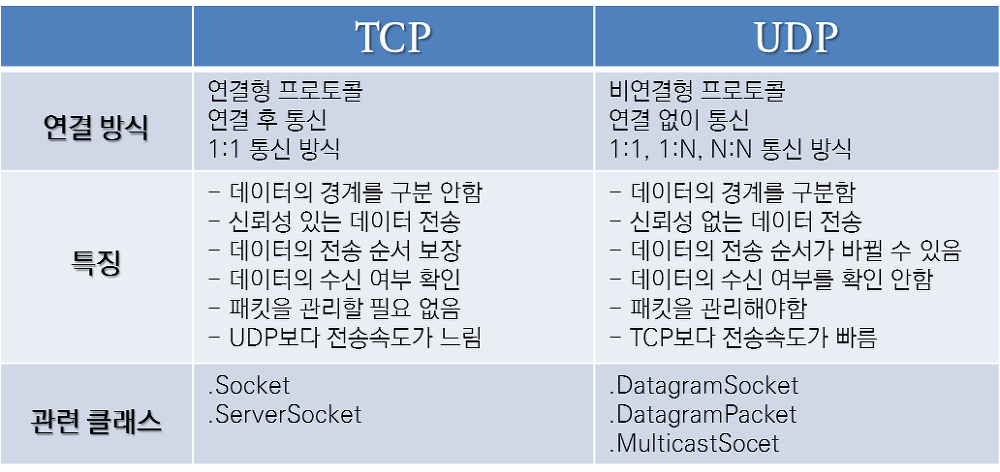
연결형 서비스를 지원하는 전송(Transport)계층 프로토콜
인터넷 환경에서 기본으로 사용
호스트간 신뢰성 있는 데이터 전달과 흐름제어 및 혼잡제어 등을 제공하는 전송계층
특징
- 가상 회선 연결 방식
- 높은 신뢰성(Sequence Number, Ack Number를 통한 신뢰성 보장)
- 실패시 데이터를 재전송함.
- 연결의 설정(3-way handshaking)과 해제(4-way handshaking)
- 데이터 흐름 제어(수신자 버퍼 오버플로우 방지) 및 혼잡 제어(네트워크 패킷 수가 과도하게 증가하는 현상 방지)
- 전이중(Full-Duplex), 점대점(Point to Point) 서비스
- 전이중: 두 통신 프로세스 간에 양방향으로 데이터가 동시에 전송될 수 있는 통신 방식
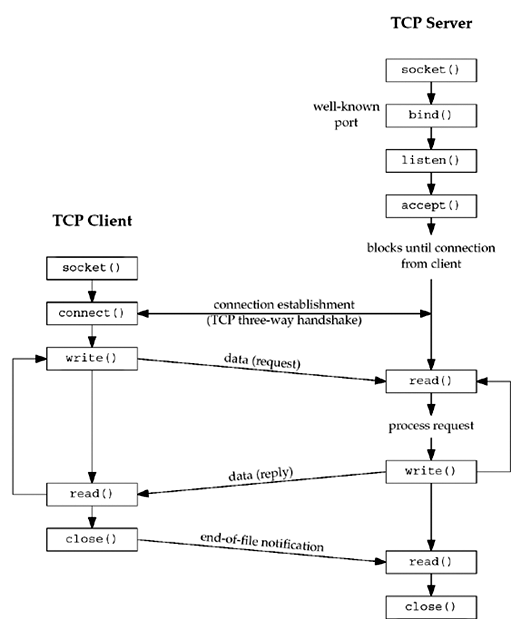
TCP Client/Server model
3-way handshaking
TCP/IP 프로토콜을 이용해서 통신을 하는 응용프로그램이 데이터를 전송하기 전에 먼저 정확한 전송을 보장하기 위해 상대방 컴퓨터와 사전에 세션을 수립하는 과정
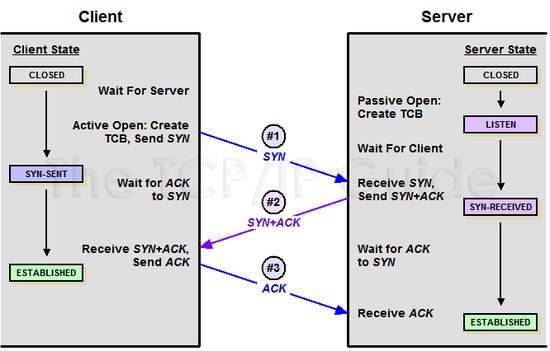
- step 01
- A Client는 B Server에 접속을 요청하는 SYN 패킷(Synchronize sequence numbers)를 보낸다. 이때 A Client는 SYN을 보내고 SYN/ACK 응답을 기다리는 SYN SENT 상태가 된다.
- step 02
- B Server는 SYN 요청을 받고 A Client에게 요청을 수락한다는 ACK와 SYN flag가 설정된 패킷을 발송하고 A가 다시 ACK로 응답하기를 기다린다. 이때 B Server는 SYN_RECEIVED 상태가 된다.
- step 03
- A Client는 B Server에게 ACK를 보내고 이후로부터는 연결이 이루어지고 데이터가 오가게 된다. 이때 B Server의 사태가 ESTABL
4-way handshaking
세션을 종료하기 위해 수행되는 절차
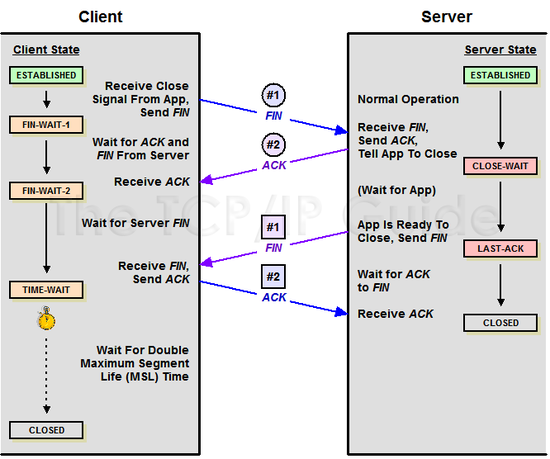
- step 01
- Client가 연결을 종료하겠다는 FIN플래그를 전송
- step 02
- Server는 일단 확인메시지를 보내고 자신의 통신이 끝날때까지 기다리는데 이 상태가 TIME_WAIT상태다.
- step 03
- Server가 통신이 끝났으면 연결이 종료되었다고 클라이언트에게 FIN플래그를 전송한다.
- step 04
- Client는 확인했다는 메시지를 보낸다.
Sample TCP Server
import socket
import sys
# 1. Create a TCP/IP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 2. Bind(Associate the socket with the server address) port number: 10000
server_address = ('localhost', 10000)
sock.bind(server_address)
# 3. Listen for incoming connections
# listen() puts the socket into server mode
sock.listen(1)
# 4. accept() waits for an incoming connection
while True:
# Wait for a connection
print("Waiting for a connection")
connection, client_address = sock.accept()
"""
accept() returns an open connection b/t server and client along with the address of the client.
"""
try:
print('connection from ', client_address)
# 5. Receive the data in small chunks and retransmit it
while True:
data = connection.recv(16)
print("received '%s'" % data.decode())
if data:
print("sending data back to the client")
connection.sendall(data)
else:
print("no more data from ", client_address)
break
finally:
# 6. Clean up the connection
connection.close()
Sample TCP Client
import socket
import sys
# 1. Create a TCP/IP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 2. Connect the socket to the port where the server is listening
server_address = ('localhost', 10000)
print('connecting to %s port %s' % server_address)
sock.connect(server_address)
try:
# 3. Send data
message = 'This is the message. It will be repeated'
print('sending %s' % message)
sock.sendall(message.encode())
# 4. Look for the response
amount_received = 0
amount_expected = len(message)
while amount_received < amount_expected:
data = sock.recv(16)
amount_received += len(data)
print('received "%s"' % data.decode())
finally:
# 5. closesocket
print('closing socket')
sock.close()
UDP(User Datagram Protocol)
비연결형 서비스를 지원하는 전송계층 프로토콜
사용자 데이터그램형 프로토콜
인터넷상에서 서로 정보를 주고받을 때 정보를 보낸다는 신호나 받는다는 신호 절차를 거치지 않고, 보내는 쪽에서 일방적으로 데이터를 전달하는 통신 프로토콜
보내는 쪽에서는 받는 쪽이 데이터를 받았는지 받지 않았는지 확인할 수 없고, 또 확인할 필요도 없도록 만들어진 프로토콜
특징
- 비연결형(port만 확인하여 소켓 식별 및 송수신)
- 패킷 오버헤드가 적어 네트워크 부하 감소
- 비신뢰성
- 오류검출(헤더에 오류 검출 필드를 포함하여 무결성 검사)
- TCP의 handshaking같은 연결 설정이 없다
- DNS, NFS, SNMP, RIP 등 사용
Sample UDP Server
import socket
import sys
# 1. Create a TCP/IP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# 2. Bind(Associate the socket with the server address) port number: 10000
server_address = ('localhost', 10000)
sock.bind(server_address)
# 3. recvfrom()/sendto()
while True:
print("Waiting to receive message")
data, address = sock.recvfrom(4096)
print('received %s bytes from %s' % (len(data), address))
print(data.decode())
if data:
sent = sock.sendto(data, address)
print('send %s bytes back to %s' % (sent, address))
Sample UDP Client
import socket
import sys
# 1. Create a TCP/IP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
server_address = ('localhost', 10000)
message = 'This is the message. It will be repeated'
try:
# 2. Send data
print('sending %s' % message)
sent = sock.sendto(message.encode(), server_address)
# 3. Receive response
print('waiting to receive')
data, server = sock.recvfrom(4096)
print('received "%s"' % data.decode())
finally:
# 4. closesocket
print('closing socket')
sock.close()
TCP vs UDP